
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is the technique of improving the performance of a website by modifying its structure and content in order to enhance visibility and web traffic. It improves website quality and raises viewer-to-customer conversion rates.
It is an important part of digital marketing that focuses on increasing the visibility and rating of a website in search engine results pages (SERPs). SEO’s primary purpose is to increase organic (non-paid) traffic to a website by boosting its relevance and authority in the eyes of search engines. This SEO tutorial covers a to z SEO basics.
SEO Education is designed to serve both beginners and professionals.
1) Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
1.1) What is SEO?
SEO, or Search Engine Optimization, is the practice of increasing (optimizing) the visibility of a website/webpage on search engines like Google and Bing.
The higher your pages rank in search results, the more likely they will be noticed and clicked on. The goal of Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is to attract website visitors who will eventually become consumers, clients, or a devoted audience that returns on a regular basis.
1.2) Why do we need SEO?
We require Search Engine Optimization for the following aspects:
To enhance the quality of our website.
To enhance online traffic and visibility.
To enhance the customer experience
To acquire a competitive advantage.
To analyze and monitor the website.
Suppose you have a website that deals with one of the following:
Products you sell.
Services you offer.
Information on issues in which you have extensive knowledge and experience.
Assume you don’t use Search Engine Optimization (SEO) and your website ranks at 45 in the Google Search results, resulting in 100 unit conversions. On the other hand, the website that ranks first on Google for the identical product has a 10,000 conversion rate. So think about it: you are losing around 9,900 potential customers just because you are not in the first position. This is the main reason why we need SEO.
1.3) Basics of SEO
Keyword research: Determine which keywords are most relevant to your target audience. Use tools such as Google Keyword Planner, SE Ranking, SEMrush, or Ahrefs to choose keywords with a suitable combination of search volume and competitiveness.
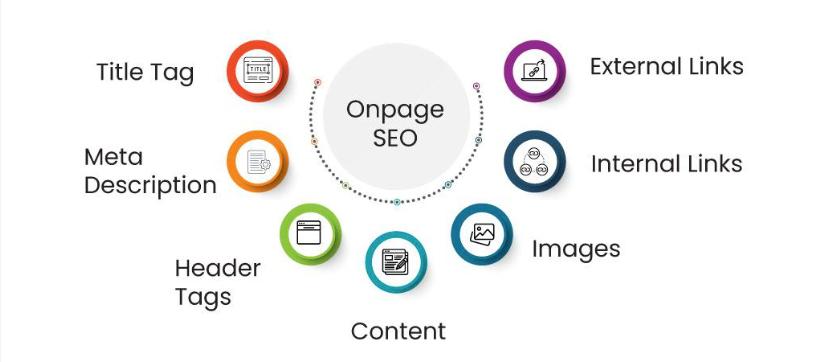
On-page SEO involves optimizing your content and HTML source code for search engines. Include your target keywords in the title tag, meta description, headers, and throughout the text. Ensure that your website’s structure is clear and organized, with easy navigation. Website SEO checkers, such as SE Ranking, can help you identify areas for improvement and optimize your website for higher ranks.
Quality Content: Create high-quality, relevant content for your audience. Regularly update your material to keep it current and relevant. Use a range of content formats, including text, photographs, videos, and infographics.
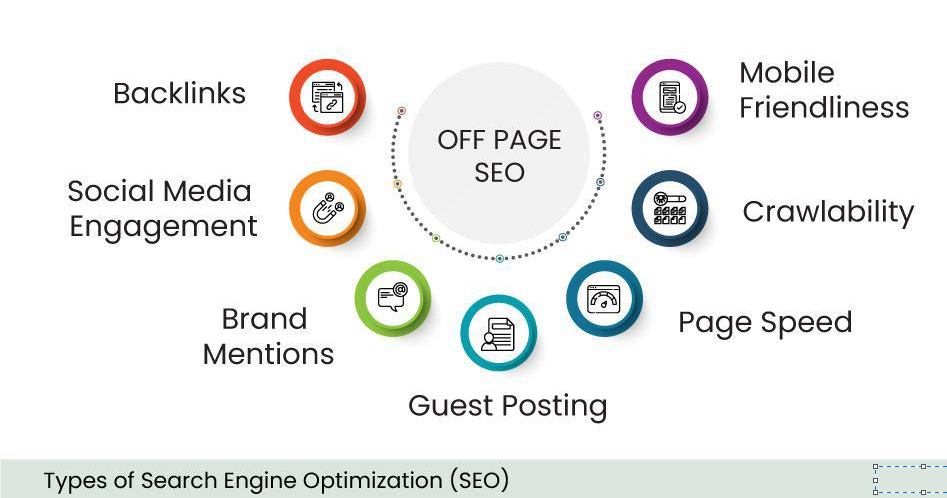
Off-Page SEO: Create high-quality backlinks from credible websites to boost your website’s authority. Engage with social media to boost your online presence and market your content. Encourage social sharing and involvement.
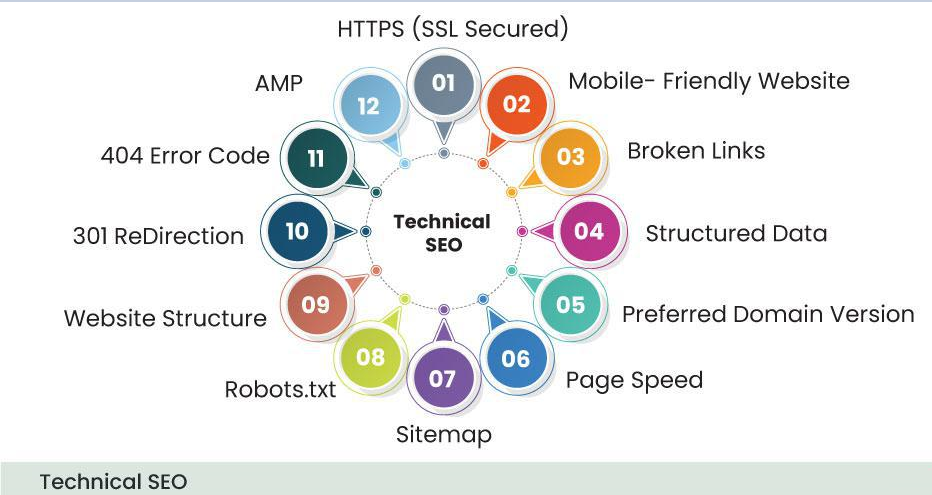
Technical SEO: Ensure that your website is technically sound and easily crawlable by search engines. Optimize page speed to improve user experience and search engine ranking. Implement a mobile-friendly design, which is an important ranking factor.
User Experience (UX): Make sure your website offers a smooth user experience. Improve the site’s navigation and structure so that users can easily discover information. Reduce bounce rate by providing entertaining and relevant content.
Analytics: Utilize technologies like Google Analytics to analyze your website’s performance. Keeping track of essential metrics like organic traffic, conversion rates, and keyword rankings. Analyze data to make the best judgments.
1.4) How Does SEO Work?
The most crucial topic to cover in this SEO Tutorial is how SEO search optimisation works. SEO works by optimizing different aspects of a website to make it more accessible to search engines, resulting in increased visibility and ranking in search engine results pages (SERPs). The goal is to drive more organic visitors to the website.
Search Engine Crawling: To browse the web, search engines such as Google use automated bots known as spiders or crawlers. These bots follow links from one page to the next, discovering and indexing content on websites.
Indexing: After a page is crawled, the content is examined and saved in the search engine’s index. The index functions as a huge library catalog that the search engine refers to when users Enter your search query.
Ranking Algorithms: Search engines employ sophisticated algorithms to estimate the relevance and authority of indexed sites for specific search queries. Algorithms analyze a variety of variables, including keyword relevance, content quality, user experience, backlink profile, and others.
Keyword Relevance: Search engines determine how well a page’s content matches user search queries. Keyword optimization is the strategic use of relevant terms in titles, headers, meta tags, and throughout the text.
Material Quality: The quality of material is critical. Search engines attempt to provide users with quality, informative, and interesting material. Content that meets user intent and gives a thorough response to a query is more likely to rank higher.
Backlinks, also known as inbound links, are links from other websites to your site. They convey a sense of trust and authority. High-quality, relevant backlinks can improve a website’s rating.
1.5) How Does Google Makes Money?
Google produces money through a variety of avenues, and while search engine optimization (SEO) does not directly contribute to Google’s revenue, it is an important part of Google’s overall business plan.
Here’s how Google gets revenue and how SEO indirectly helps it:
Google’s principal revenue source is advertising, specifically through its Google Ads network.
Businesses pay to have their ads displayed on Google’s search engine results pages (SERPs) and throughout its network, which includes websites and apps that are members of Google Display Network. Google Ads allows businesses to bid on relevant keywords for their products and services. When consumers search for specific terms, the advertisements display at the top of the search results page.
The advertisements are often labeled “ads” and appear apart from the organic search results.
Google Ads uses a pay-per-click (PPC) approach, meaning advertisers only pay when users click on their ads.Google Analytics and Search Console offer tools for analyzing website performance, user behavior, and search queries, including keyword data.
While these tools are free to use, they indirectly benefit Google’s ecosystem by offering important data and insights to website owners, which may influence advertising decisions.
AdSense and AdMob
Google AdSense allows website owners to show Google Ads on their sites and earn money when users click on them.
AdMob is a comparable platform for mobile apps that allows developers to monetize their apps with in-app ads.Google owns YouTube, a leading video-sharing network.
Google Ads allows businesses to run ads on YouTube, which generate revenue for Google when users interact with them.
2) Role of Search Engine in Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
2.1) What is a search engine and how does it work?
Search engines are applications that let users find and obtain information from the massive amount of content available on the internet. They utilize algorithms to index and rank online sites based on their relevance to a user’s query, displaying a list of results for users to browse. Google, Yahoo, and Bing are among the most popular search engines.
2.1.1) How search engines work:

Crawling: Search engines utilize automated programs known as crawlers or spiders to navigate the web. These crawlers begin by visiting a list of known web pages and then following links on those pages to find new ones. The crawlers download the content of the web pages they visit and then follow the links on those pages, repeating the process to find new information.
Indexing: The information gathered by the crawlers is arranged and stored in a huge database known as an index.
The index contains information about each page, including keywords, content, meta tags, and links.
Processing and Ranking: When a user inputs a search query, the search engine evaluates it and returns relevant results from its index. Algorithms are used to rank the results based on the index. These results are ranked using algorithms that take into account a variety of characteristics such as relevance, content quality, user experience, and website authority.
Retrieval and Display: The search engine finds the most relevant pages in the index and presents them on the search results page. The displayed results frequently include a title, a snippet (a short summary of the website), and a URL.
User Interaction and Feedback: Search engines collect information about user interactions, such as which results users click on, how long they spend on a page, and if they refine their search. This data helps to enhance the search engine’s algorithms over time, making the results more accurate and relevant.
The majority of search engines provide guidance on how to improve your page ranking, but the specific algorithms are highly guarded and frequently revised to prevent exploitation.
2.2) Search Engine Results Page (SERPS)
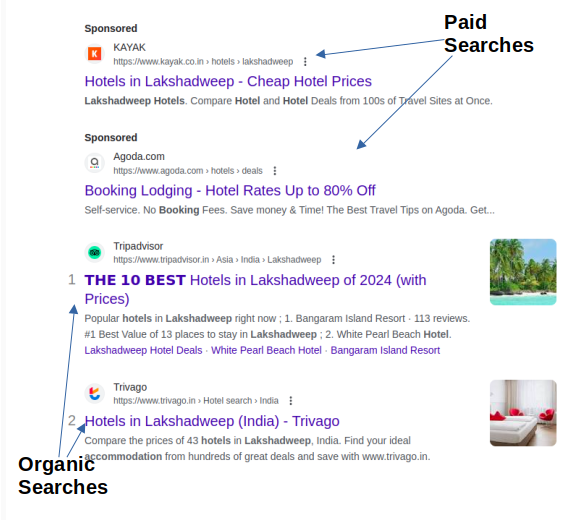
A search engine results page, or SERP, is the page that appears after a user types a search query. A Search Engine Results Page (SERP) includes several links that are related to the user’s query. It displays the paid searches that appear at the top of the SERP. Google is continually refining its algorithm to offer the best results; thus, it is critical to stay current with Google algorithm upgrades.
Paid Searches: Paid Searches are typically displayed at the top of SERPs. Paid searches are ads. Search engines will display advertisements close to
Paid Searches: Paid Searches are typically displayed at the top of SERPs. Paid searches are ads. Search engines will display ads alongside organic search results. This is the primary way search engines generate revenue.
Organic Searches: Organic Searches are the unpaid portions in the search engine results page (SERP) that are determined by the content’s relevancy to the keyword query rather than by search engine marketing.
Do all search engines work on the same principle?
Although most search engines operate on the same basic premise, there are subtle variances that cause significant differences in their results. For example, Yahoo and Bing prioritize on-page keyword criteria, but Google prioritizes links and hyperlinks. Also, Google’s rankings of a website are heavily influenced by its primitiveness, i.e., how old the website is, as opposed to Yahoo, which gives little or no preference to the primitiveness of the website; thus, to improve a website’s ranking in different search engines, a slightly different procedure must be followed.
3) Types of Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
There are numerous sorts of search engine optimizations (SEOs); however, the following are some of the most common:

On-page SEO: On-page SEO is the process of optimizing individual web pages to increase their ranking in search engine results pages (SERPs). It is a sort of SEO that entails optimizing several aspects of a website to make it more relevant and appealing to search engines and visitors.
Off-Page SEO: Off-Page SEO refers to the practise of building backlinks and managing social media presence.
Technical SEO : Technical SEO relates to website and server optimization that assists the crawler in crawling, indexing, and ranking activities, allowing your website to rank higher.
Local SEO : Local SEO, or local search engine optimization, aims to boost a website’s visibility in local search results. It is a subset of SEO that focuses on making a website or online presence more search engine friendly for local search terms.
Mobile SEO: Mobile SEO is the practice of optimizing a website for mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets. The primary goal is to ensure that the website is completely functioning and organized on mobile devices.
Voice SEO: Voice SEO is the practice of optimizing a website to appear in voice search results; this is significant because people rarely speak things the way they write them.
Mobile SEO: Mobile SEO is the practice of optimizing a website for mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets. The primary goal is to ensure that the website is completely functioning and organized on mobile devices.
Voice SEO: Voice SEO is the practice of optimizing a website to appear in voice search results; this is significant because people rarely speak things the way they write them.
Image SEO: Image SEO is the practice of optimizing images to appear in image search results. The primary goal is to get our photographs crawled and ranked highly in search results.
Ecommerce SEO : Ecommerce SEO refers to the process of enhancing an online store’s exposure and organic rankings in search engines such as Google and Bing.
International SEO : International search engine optimization, or international SEO, is the activity of optimising your website for search engines so that they can quickly determine which countries and languages you employ for business.
Enterprise SEO : Enterprise SEO refers to the process of improving a significant company’s search engine rankings. Scaling content, ongoing technical SEO management, and automation are standard enterprise-level SEO tactics.
4) Types of Search Engine Optimization (SEO) Techniques
4.1) Black-Hat SEO


Black Hat SEO is defined as unethical and manipulative tactics used to deceive search engines and artificially boost a website’s search engine ranks. These strategies violate search engine restrictions by leveraging algorithm flaws to get rapid, generally short-term gains. While black hat SEO strategies can result in immediate ranking improvements, they also carry major dangers, such as potential fines, loss of trust, and long-term damage to a website’s online presence.
Black Hat SEO uses the following SEO techniques:
Keyword Stuffing: Keyword stuffing is the technique of cramming your content with irrelevant keywords in order to improve your site’s ranking on search engine results. However, the page will rank for irrelevant terms, which will be very aggravating to users.

Doorway Pages: These are the undesirable pages that serve as a bridge between the actual content and the audience. These are designed to rank highly for specific keywords that have nothing to do with the user.

Content Automation: Content automation is the process of creating content without the involvement of humans, i.e., by the use of machines. The idea is to develop material that is more search engine friendly while not focusing on the user’s demands.
Hidden Texts/Links: These are misleading types of links that are nearly invisible to users. Web pages with hidden links incorporated in them appear to be conventional pages; nevertheless, these hidden links are not examined.
It can be accomplished in the following ways:
1. Using the same color for the text and background.
2. Resize the font scale to zero.
3. Hide behind the image
4. Placing the link on little characters such as commas, colons, etc.
Duplicate content: Duplicate content is one of the most popular Black Hat SEO methods. Even Google has altered its algorithm to determine whether the content on your site is original or copied from another site. Google always prefers original content.
Sneaky Redirects: This is the process of redirecting users to a different URL than the one they requested. However, there are legitimate reasons to redirect a visitor from one URL to another, but it is typically used for malevolent purposes.
Cloaking: Cloaking is the process of displaying alternate material to consumers and search engines. For example, if you search for the keyword “mathematics” and then visit the related website, you will be redirected to an entirely different material.
Paid Links: Yes, Paid Links are also considered Black Hat SEO because if you try to increase your domain authority by selling links, Google will de-index your website. Many other Black Hat SEO tactics violate Google’s standards.

4.2) White-Hat SEO

White-hat SEO is an ethical way to optimize your website for search engines. It tries to increase your site’s search engine rankings while still offering a good user experience by adhering to recognized principles and best practices.
White-hat SEO uses the following techniques:
Create high-quality, relevant, and useful material for your target audience. Regularly update and renew your content to keep it relevant and informative.
Keyword Optimisation: Conduct keyword research to uncover relevant and popular keywords. Include keywords in your content, titles, headings, and meta tags.
Title and Meta Description Optimization: Create an appealing and relevant title and meta descriptions for each page. Ensure that they appropriately reflect the page’s content and encourage users to click.
Quality Backlinks: Create natural backlinks to respected and relevant websites. Instead of engaging in deceptive link-building tactics, focus on earning links by creating valuable content.
User Experience (UX): Design a user-friendly website with a straightforward navigation structure. Optimize page loading time and make sure your website is mobile-friendly.
Optimize your website for mobile devices to ensure a seamless experience for mobile users.
Social Media Presence: Connect with your target audience on social media sites. Share your material on social media to boost visibility and reach.
Site Structure and Navigation: Make sure your website has a clear and ordered structure. To help search engines index your information, develop clear and descriptive URLs and a sitemap.
Internal Linking: Use internal links to connect relevant content on your website. This helps search engines understand your website’s structure and facilitates user navigation.
Responsive Design: Make your website responsive and adaptable to various screen sizes and devices.
5) SEO Tools
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) tools are intended to boost your website’s rating on search engine results pages (SERPs). These tools provide useful SEO insights for your website and assist you in identifying the best techniques for improving its rating. Google Analytics, SEMrush, Ahref, MOZ, Google Search Console, and SE Ranking are some of the most popular SEO tools for website owners.
Key topics:
5.1) Google Analytics
Google Analytics is the most famous and free SEO tool for analyzing and tracking your website traffic and it gives you access to a wide range of data that you can use to improve your SEO
Features of Google Analytics:
- To further segment data and explore, include supplementary dimensions in your reports.
- You can segment data results using advanced filters so that you can concentrate on what matters to you.
- Pivot view enables you to quickly generate a pivot table from the data without exporting it to Excel and Google Sheets.
5.2) SEMrush
SEMrush is the best all-in-one SEO tool you need and it is the most famous SEO tool in the market. It offers us all the tools that we need to create high-quality content for our website.
Features of SEMrush:
- Analyzing the competitor keywords and ad budgets
- Find the right keywords for SEO and PPC campaigns
- Conduct deep link, bulk analysis
- Analyze the media consumption and behavior of your potential customers
5.3) Ahref
Ahref is a software tool that helps in link building, keyword research, competitor analysis, rank tracking and site audits.
Features of Ahref:
- Ahrefs helps you find the best words to use on your website so that people can easily find you on search engines.
- It shows you who is linking to your website, which is like getting recommendations from others on the internet.
- Ahrefs checks your website for any issues that might affect how it appears in search results. It’s like a health check for your site.
- It lets you know where your website stands in search results for specific keywords. It’s like keeping an eye on your position in the popularity contest of the internet.
5.4) MOZ
Moz is one of the top SaaS SEO tools that professionals use. Moz is a full-service, all-around powerhouse tool, whether you are looking for keyword suggestions or want to crawl the website.
Features of MOZ:
- It helps to track search engine ranking for specific keywords over time.
- It checks the website for technical SEO problems including duplicate content, broken links, and slow page loads.
- It provides details on the quantity and quality of backlinks or links from other websites to the website of the user.
- It identifies the keywords that will rank the website in search engine results.
6.5) Google Search Console
Google Search Console is a tools used to check indexing status, search queries, crawling errors and optimize visibility of their websites
Features of Google Search Console:
- Shows how often your site appears in Google search results and which queries lead people to your site. It’s like seeing how popular your website is.
- Lets you check how a specific page on your website appears in Google’s search results. It’s like looking at how your page shows up when someone searches for it.
- Allows you to submit a sitemap of your website to Google. A sitemap is like a map that helps Google find and understand all the pages on your site.
- Highlights any issues Google has in crawling and indexing your site. It’s like finding and fixing problems that might stop Google from showing your pages.
- Checks if your website is mobile-friendly. It’s like making sure your site looks good and works well on phones and tablets.
